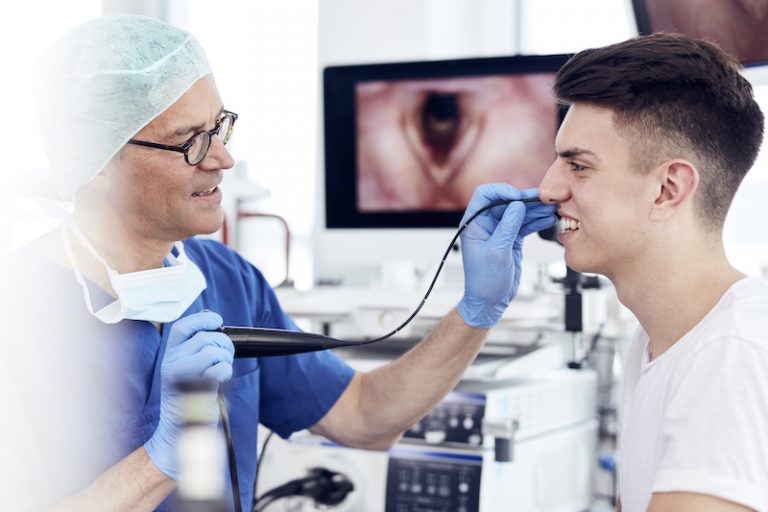
The MEDICAL VOICE CENTER has all diagnostic devices, tools, and instrumentation that are needed to comprehensively assess, examine and test human voice function for speech, singing, and artistic voice use. Another advantage is the possibility of examining patients and clients in an ambulatory multidisciplinary setting – in one day.
After thorough diagnosis an individualized counsultation, therapy or rehabilitation program will be offered.
The latest very high resolution chip-on-the-tip flexible endoscopes, top quality rigid laryngoscopes and high end computer image analysis programs are routinely used. For rigid endoscopy we prefer 70° optics combined with HD three chip cameras, for flexible endoscopy the latest and thinnest high quality flexible endoscopes are applied. All endoscopy is absolutely painless – even babies and children can be ‚scoped’ without discomfort.
Vocal fold vibrations are analysed with high end LED illumination – the sound-triggered bright stroboscopic light flashes are used for monitoring vibrational patterns of the vocal folds. We regularly take advantage of this technology also to assess amplitudes, modes of vibration, and other phenomena related to voice production.
Optical light filtering with NBI and technical spectral enhancement coding is used to contrast images. This enables and facilitates the detection of tissue changes of small vessels (capillaries) in diseases such as papilloma, dysplasia, cancer, and other morphological changes. NBI is also used for detection of problems during swallowing (penetration and aspiration of food and liquids).
With more than 4,000 image frames recorded every second (!), visualization of even slightest changes of vocal fold vibratory function is enabled. High speed imaging, also called high speed glottography, is superior to stroboscopy in cases of asymmetrical vibratory patterns, irregularities during voice production and unusual solitary movements of the endolarynx.
The combination of CCD imaging and line kymography allows for a differentiation of vocal fold vibration according, especially when comparing the left vocal fold with the right vocal fold. A great advantage is the 2-dimensional display of several vibrational cycles within one graph. Thus, videokymography facilitates to find the more affected side of vibrational disturbance by ist visual demarcation.
Biosignal analysis with electroglottography (EGG) provides a time resolution of vocal fold contacting in the order of magnitude of milliseconds. The easiness of application makes it the most robust technology for the detection of fundamental frequency (F0).
Furthermore, time based regularity and periodicity of vocal fold vibrations can easily be assessed with a high grade of precision.
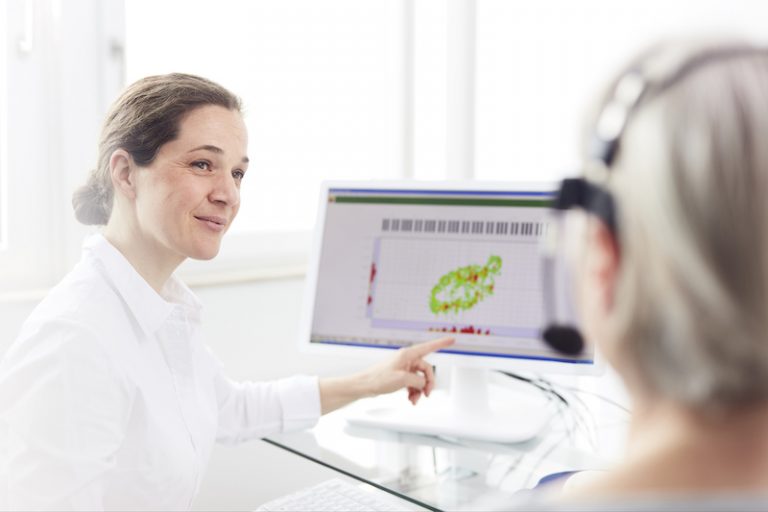
Voice assessment with computer technology includes, e.g., broad band and narrow band spectral analysis, formant analysis, perturbation measurement, signal-to-harmonics ratio, F0 detection and many more parameters of voicing.
Simultaneous presentation of electroglottographic (EGG) and microphone signals, power spectrum of spoken and sung sequences, and highlighting of singing formants is a powerful tool for analyzing singing techniques and enabling easy-to-interpret visual feed back by displayed voice graphs on a PC-based monitor.
Determination of frequency voice ranges and sound pressure levels is an important tool to assess the potential of the functionality of the voice and it’s stamina. Running speech, singing voice and shouting can be measured and compared with normative data.
Professional voice users have to rely on longterm voice quality and durability. Vocal loading tests assess patient’s voice quality before, during and after using their voices loud enough to be compared with professional daily voice use.
Voice loading tasks have a long tradition in Europe, and normative task conditions should (and can) be adapted to the individual’s specific circumstances.
Logopedic comprehensive assessment of breathing patterns, phonatory abilities, resonance strategies, postural habits and psychological conditions for the individual voice imaging will be assessed. Examination of RBH and GRBAS perceptual voice quality as well as many other objective and subjective examinations are at hand in the logopedic diagnostic session.
Detailed laryngeal and paralaryngeal muscle activity can be measured directly with the use of finest electrodes, placed inside the muscles transcutaneously, such as in cases of bilateral or unilateral recurrent nerve paralysis and paresis (RLN paresis and RLN paralysis).
LEMG is also used for precise placement of injection cannulas when botulinum toxin injections are needed.
Breathing pattern assessment, measurement of maximum phonation time (MPT), pneumotachographic lung volume examination are important parameters within aerodynamic testing.
Semi occluded mouth and airway voicing (such as in LaxVox or other methods) rely on a certain amount of air control in phonation and quiet breathing.
Voicing and swallowing rely on a good muscular function of the hypopharynx and larynx. With flexible endoscopes a functional endoscopic examination of swallowing (FEES) can be performed in the office – without anesthesia and absolutely painless.
Swallowing of solid food and liquids can be assessed with tracing of the food bolus along the upper airways. Swallowing disorders with drooling, leakage, retention, penetration, aspiration, regurgitation within the oral and pharyngeal phases (predeglutitive, intradeglutitive, postdeglutitive) are visualized with food colourants.
After a laryngeal videoendoscopic examination, a thin flexible endoscope is passed into the upper esophagus. This painless procedure is induced while swallowing of a cup of water – esophagoscopy enables the examiner to inspect the inside of the esophagus, thus gaining information about the mucosal lining of the esophagus and possible disorders.
TNE is a routine procedure in ear-nose-throat diagnostic services in the USA and is coming more and more to the European continent.
After a laryngeal videoendoscopic examination, a thin flexible endoscope is passed through the glottis into the upper trachea. This painless procedure is performed under topical anesthesia and enables the examiner to inspect the entire trachea down to the main bronchi.
TNT is a routine procedure in some ear-nose-throat diagnostic services in the USA and is coming more and more to the European continent.
Very many voice disorders are associated with muscular imbalance, tension, strain, and injury. Thus, symptoms can range from a lump-in-the-throat feeling to chronic pain. With the use of specific laryngeal osteopathy techniques according to Jacob Lieberman, DO, these muscular problems can be detected and target oriented, specific therapeutic programs can be applied immediately to release tension and relax muscles – and frequently one to three therapy seesions may lead to a complete physiologic balance.
Globus has many possbile reasons. When non-laryngeal reasons are ruled out (reflux, sinusitis, allergies etc.) and no specific cause can be found, there is a very high likelihood that paralaryngeal muscles play an important role causing the symptom of feeling a lump or a resistance during swallowing – a repetitive strain injury (RSI). With special osteopathic diagnostic manouvres, these potential reasons can be detected, leading to a target-specific and rapid therapeutic strategy.
With our high definition videoendoscopes, screening of healthy people as well as follow-up of patients with dysplastic and malignant tumors is easily possible – without sedation or general anesthesia.